What is USB Type-C
- BenQ
- 2020-03-31
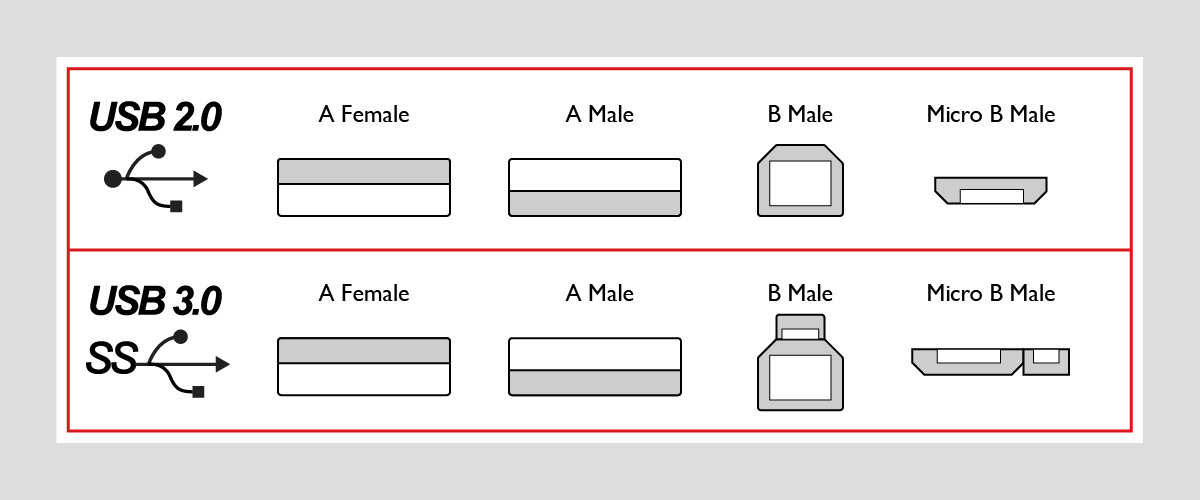
Universal Serial Bus (USB) refers to the standard serial bus that is used to connect computer systems with external devices. It also encompasses the technical specifications that govern the input/output interface which has become widespread in its use with personal computers, portable devices, and other data and communication products. In terms of form factor, USB connectors can be categorized into Type-A, Type B, and the newly added Type-C categories, with both Type-A and Type-B including sub-categories for Standard, Mini, and Micro types. Furthermore, the specifications for its supported transmissions are categorized into USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. The traditional USB Type-A and Type-B is designed to support power output of up to 100mA and data output of up to 12Mbps. These specifications have been continuously updated based on the ever-growing need for greater bandwidth and the steady evolution of multi-purpose applications. In line with that practice in April 2014 the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) launched the new USB Type-C v1.0 connector, based on the USB 3.1 standard, which offered improved bandwidth for data transmissions, support for higher power output, and other enhanced features. Shortly thereafter a wide array of consumer electronics, including Android mobile devices, notebook PCs, desktop PCs, and even gaming consoles implemented this connector in their designs.
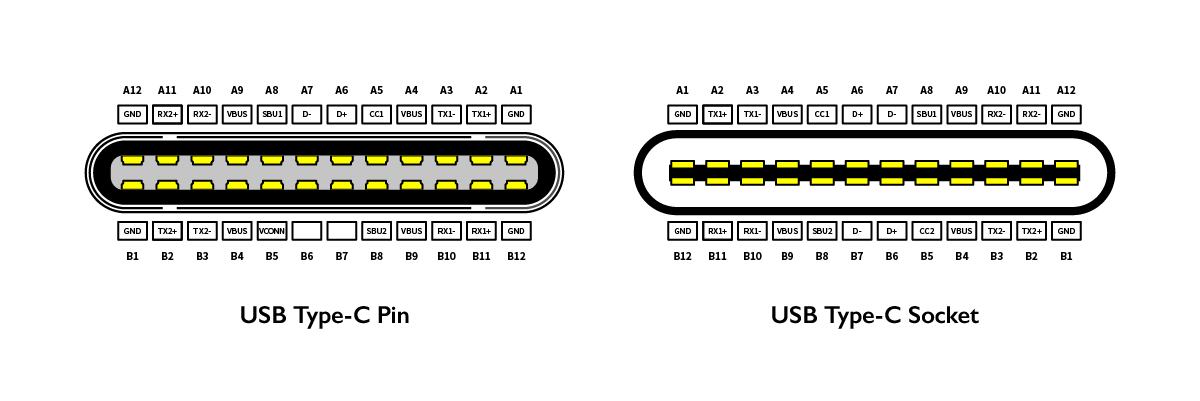
1. Power Supply: The USB Type-C interface’s built-in 5V power supply allows for it to be downwards compatible with previous USB interfaces. Beyond this the brand new USB Type-C interface also includes four pins separately used for supplying power and grounding, which allows the USB Type-C connector to support three different voltages (5V / 12 V / 20V) for a maximum output of 100W.
2. Symmetrical Connector Design: The most distinguishing feature of the USB Type-C connector design is that its top and bottom side are identical. Its connector features up to twenty-four pins and allows you to connect it in any orientation, as opposed to the traditional Micro-USB connector which only features five pins and needs the user to figure out the correct orientation to connect it. Additionally the USB Type-C connector can be connected to either the transmission or receiver end of a connection, with the degree to which its capabilities are used determined by the hardware it is connected to, all of which make plug and play with USB Type-C all the more easier.
3. Bandwidth: USB Type-C supports USB 2.0 , USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB 5Gbit/s), and USB 3.1 Gen 2 (SuperSpeed USB 10Gbit/s) data transfer speeds. The SuperSpeed USB differential signal is distributed on both sides of the USB Type-C connector so that you will be able to utilize a SuperSpeed USB data transfer connection no matter which orientation the connector is connected in .
4. Configuration Channels: USB Type-C connectors include two Configuration Channel (CC) pins which allows it to check the direction of the connection and configure the connector’s power supply, and Alternate and Accessory modes.
5. Non-USB Transmissions: USB Type-C’s support for non-USB transmissions allows OEMs to create USB Type-C connectors with custom-designed functionalities, thus expanding the boundaries for devices that employ its connectors.
As the consumer electronics, wireless device, computing, and automobile industries continue to develop an array of products and features that utilize USB Type-C technologies, the USB 3.0 Promoter Group has released device authentication protocols to deal with concerns over safety and data security and added them to the USB Power Delivery 3.0 standards. Using the USB Type-C authentication protocols, a host device can recognize and detect the product type, transfer speed, power charging specifications, and trust status of a password-enabled device or battery charger upon connection, and prevent peripheral devices from transferring unwanted data or supplying power at unsuitable levels.
Another one of the USB Type-C interface’s major features is the integration of audio/video into its transmission capabilities, meaning supported computers and/or smartphones can output an HDMI signal via USB Type-C’s DisplayPort Alt-Mode. This broadens the scope of audio/video applications for USB Type-C on mobile devices, and increases the flexibility with which users can connect their smart devices and accessories to displays and TVs. Keeping up with this trend BenQ has continually released projectors, such as the GV1 and GS2, that support DisplayPort over USB Type-C.
In response to the need for higher bandwidth caused by expanding file sizes and higher resolution video, the trend for wired connections has increasingly been to provide faster speeds and greater all-purpose use. USB Type-C is the latest attempt to become the most popular transmission interface by answering consumers’ demands for an all-in-one solution. But when all is said and done USB Type-C is just a standard for connectors; its actual functionality and capabilities will be determined by the specifications set for its transmissions. Because of all this, consumers must first understand things like the level of support for Alternate Mode (such as MHL, DisplayPort, or Thunderbolt) or Accessories Mode (the mode used for audio transmissions) technologies before they purchase a USB Type-C product. Additionally consumers need to be aware that in order for their USB 3.0/3.1 devices to be able to take advantage all the benefits of the interface, including its high transmission speeds, they need to be matched with a USB Type-C cable that conforms with USB 3.0/3.1 standards.